All the way back in the ‘80s, at the Bronx Zoo of New York Hammerhead bats, were kept in captivity. And they can be still seen at the Wroclaw Zoo in Poland.
It is also commonly called the Hammer-Headed fruit bat or the Hammerhead bat, but it has the scientific name Hypsignathus Monstrosus.
Also read: These Sand Sculptures Looks Like They have Life
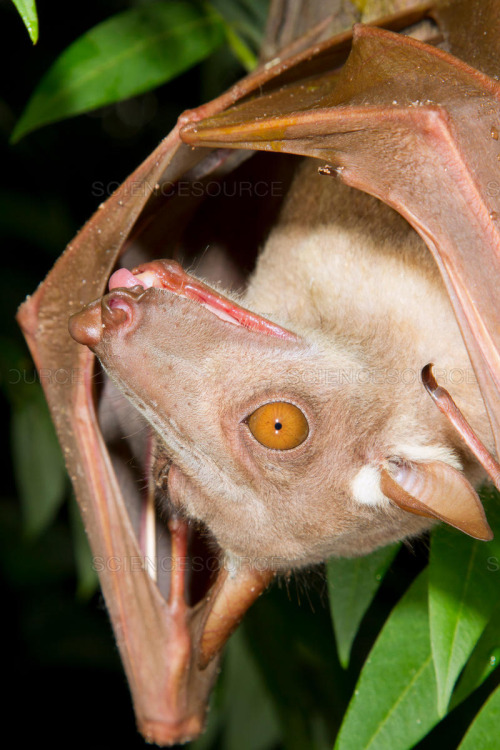
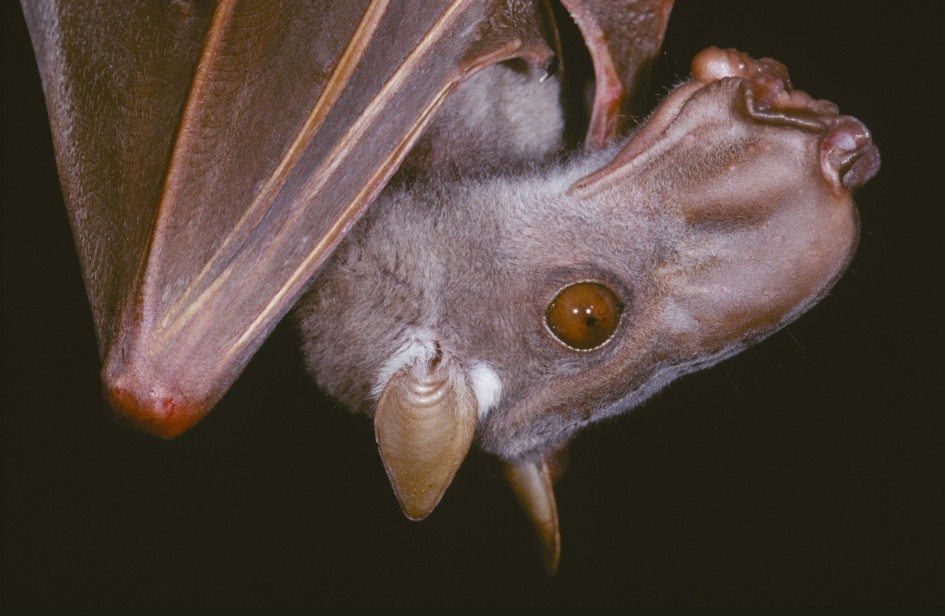
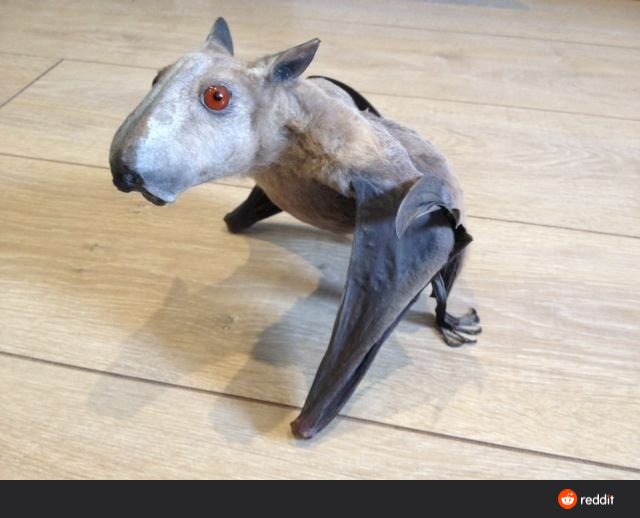
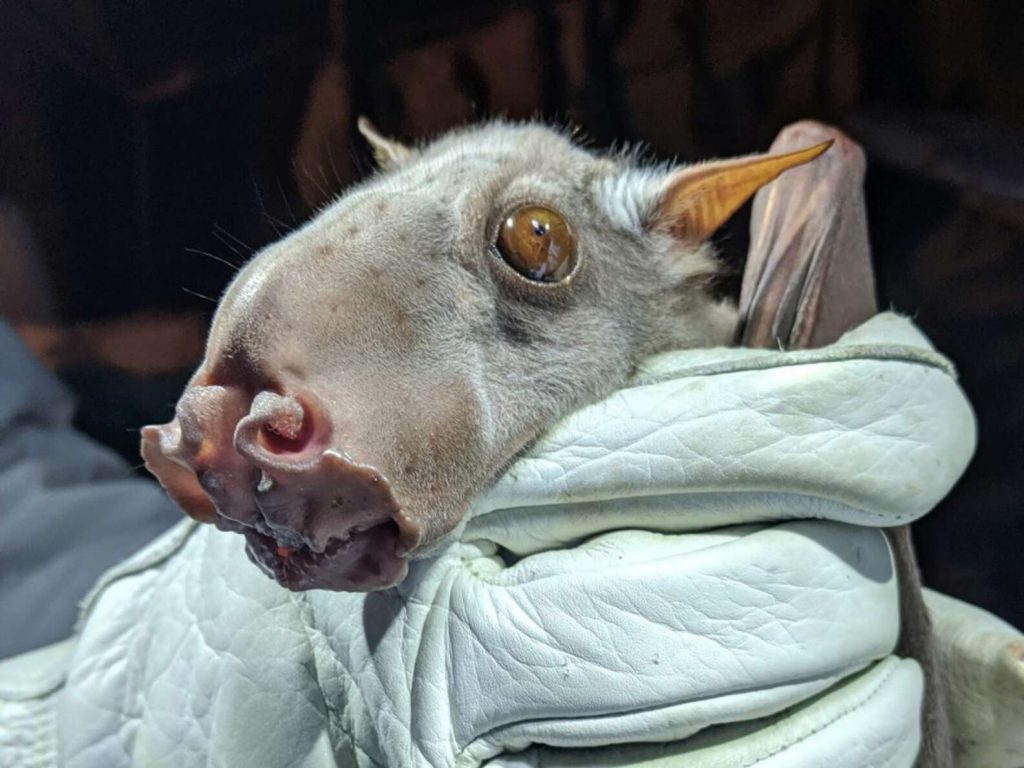
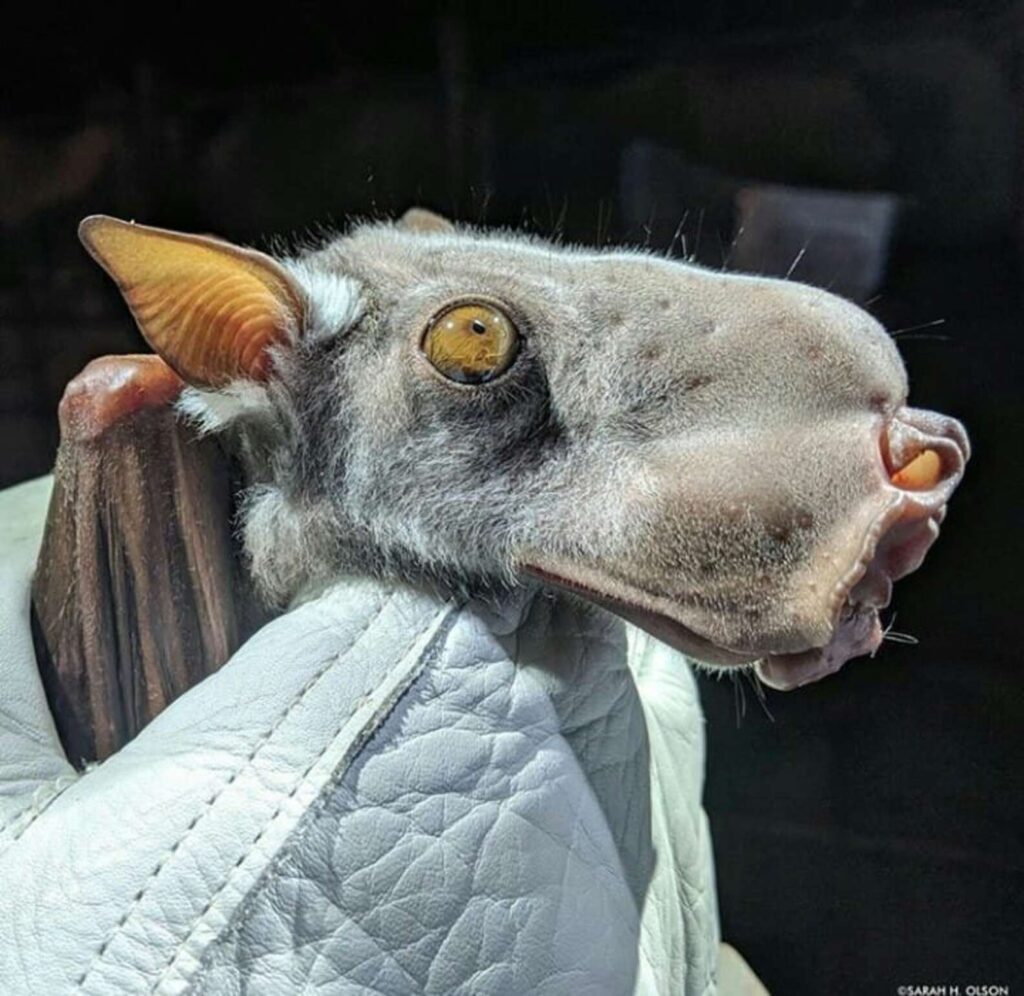
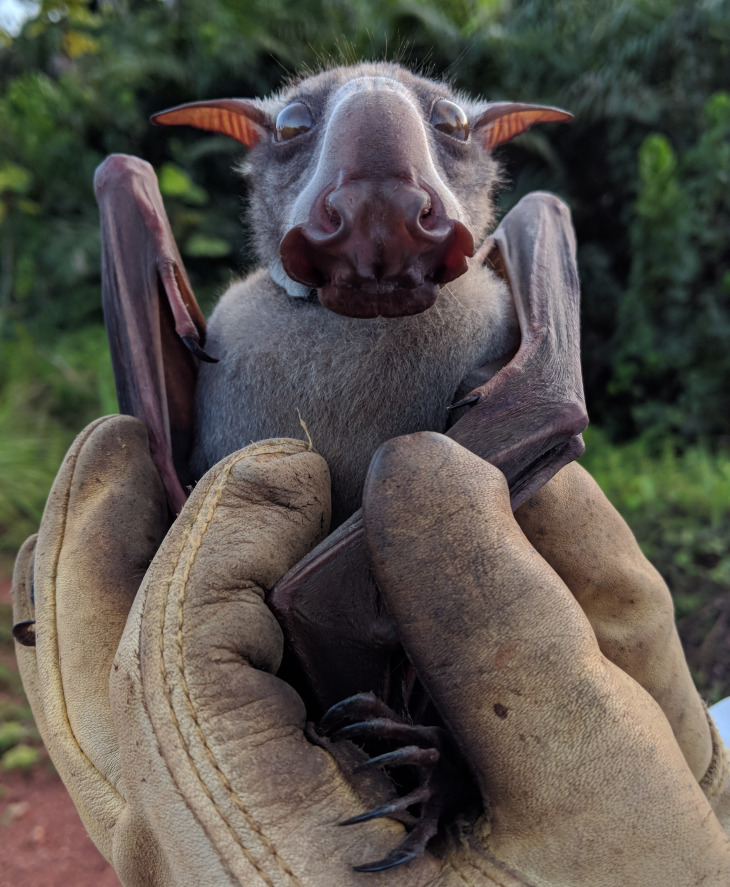
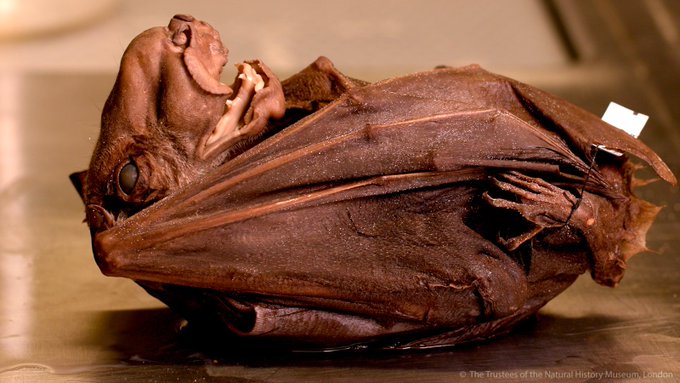
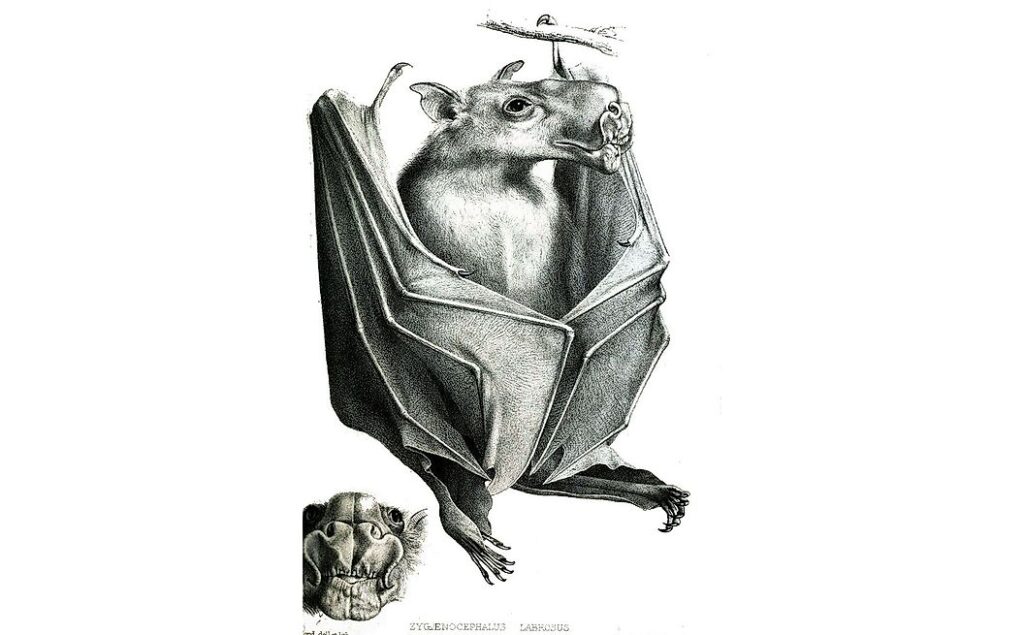
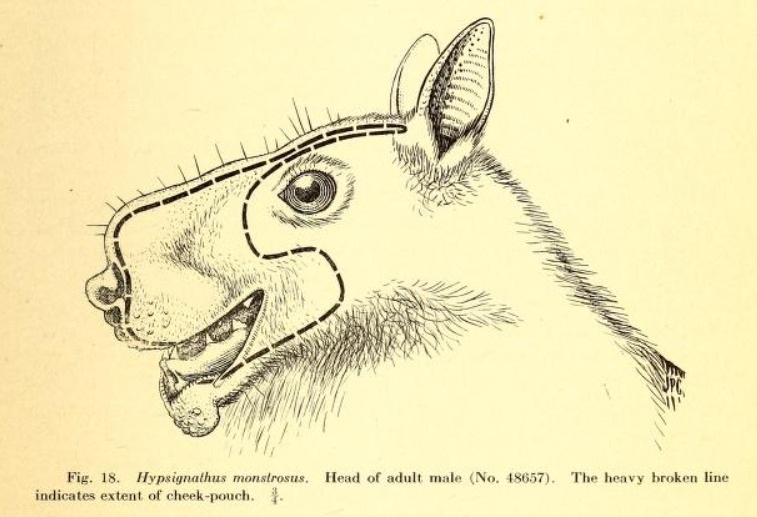
Due to the appearance of the male hammerhead bat, the scientific name of this bat species was given. It looks quite scary because of its giant snout-like resonating chamber. It is its standout feature too. The entire body of the male hammerhead fruit bats appears like any other species.
How big can a hammerhead bat grow?
It can grow up to 20 – 28 cm. It has a wingspan that can go up to 3ft (90 cm). This species is the largest bat species in all of Africa.
Hammerhead bats are often considered one of the prime nocturnal nuisances that plague the residents of equatorial Africa due to their extremely loud honks. Also, that is not without good reason. The male hammerhead bat uses its large resonating chamber on its mouth to amplify any sound it makes.
Also, males of this intriguing bat species have important internal organs like the heart and the lungs literally making room to hold their massive larynx.

Because of this strange emphasis on being loud, German zoologist Herbert Land and his partner, American ornithologist James Chapin commented about this creature, “In no other mammal is everything so entirely subordinated to the organs of voice”.
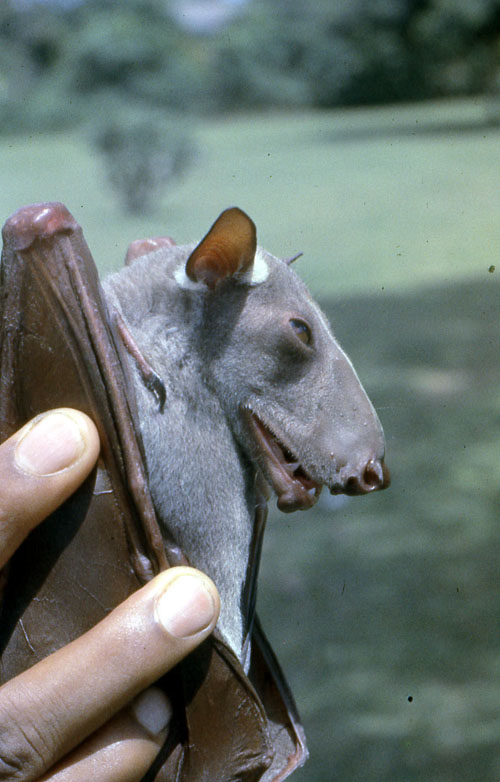
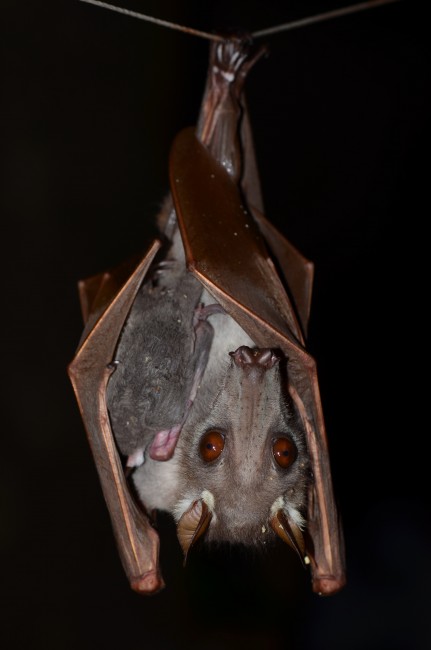
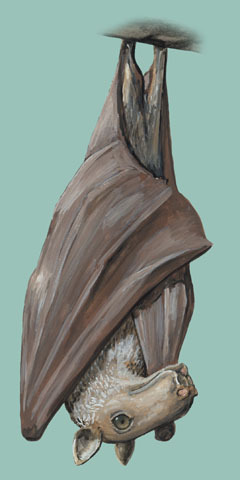
Hammerhead bats show sexual dimorphism. It means there are differences between male and female hammerhead bats that go beyond just the reproductive organs. Males are larger than the size of a female bat. And a male bat can weigh as much as twice the size of a female bat. By far the unusual-looking head of male bats is the most marked difference between males and female bats of these hammerhead bats. This unusual bat head features a large protrusion of the snout, lips, and chin to accommodate for a resonating chamber.
But when it comes to the female hammerhead bats, they possess a square head. And their mouth is as same as most other species of bats. Both male and female hammerhead bats have a strip of white fur on their back from shoulder to shoulder, and white bases of the ears.

This hammerhead bat was recently found to be the faster animal in the world. It has the ability to fly at 100 mph (161 km/h)
But due to the large size of this bat, that speed is not achievable. So it’s maximum flight speed is more likely around 50-60 mph (80-100 km/h) range. That is definitely nothing to scoff at. These bats are frugivorous animals. That means their diet mostly consists of fruits.
They can become a pesky crop pest for farmers on the continent. Because Figs are a major part of their diet. But, they also eat other African fruits such as mangoes, guavas, and bananas.
Where does a hammer-headed bat live?
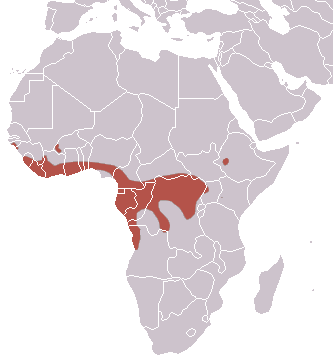
They live in rainforests with a well-established source of water, such as in swamps, mangroves, and riverine rainforests. The area of intersection of grassland and rainforest can become home for these hammerhead bats.

There are few records that have been posted in the savannahs of Africa (alongside Wildebeest, a common sight there). But that is considered due to vagrants. Not because it is an alternate habitat for Hammerhead bats.
How long do hammer-headed bats live?
They are lowland species. That means they always live around 1,800m (5,900 ft) below sea level. In their habitats (forests) it is recorded that they live for up to 30 years. These creatures are widely regarded to be the only species that demonstrate lek mating behavior.
According to Wikipedia, lek mating is an aggregation of male animals gathered to engage in competitive displays and courtship rituals, known as lekking, to entice visiting females which are surveying prospective partners with which to mate.
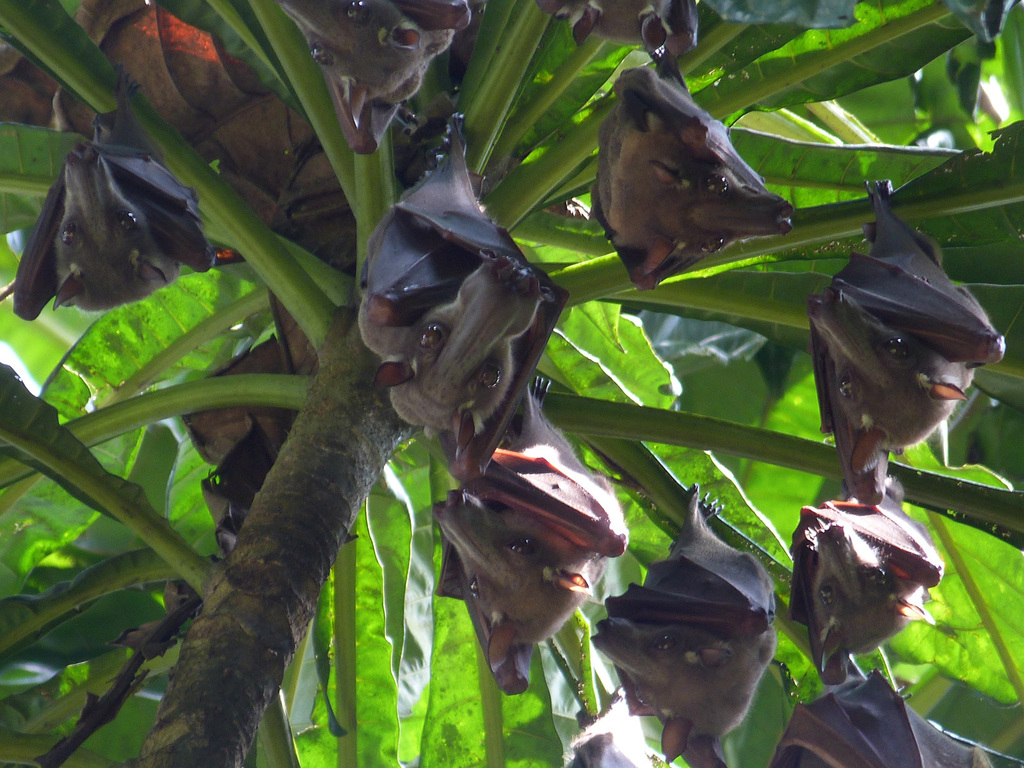
In this lek mating form, a large group of male bats (in groups of 25 -132 individual bats) will occupy a region, usually a river bed or similar place like that, and then try to attract female bats using boast behavior such as honking and flapping their wings.

There are two sessions of mating each day. Most copulation occurs in the morning session. And in the night session, most of the time male bats fight over a favorable spot in the lek. Among all the male bats 6% are successful male bats and they account for 79% of all mating activity goes to show how important a good, central spot in the lek can be.
Would they make a good pet?
These Hammerhead bats are commonly affected by parasites like mites and fleas. Also, they are not the most pleasing of animals to look at. Even though no evidence has been found so far, they have received a lot of attention and research for being the possible natural host of the Ebola virus.
But some may find this odd appearance of hammerhead bats to be cute, but you should know that a bat is an animal to be left in the wild.
Here are some photos of these Hammerhead bats